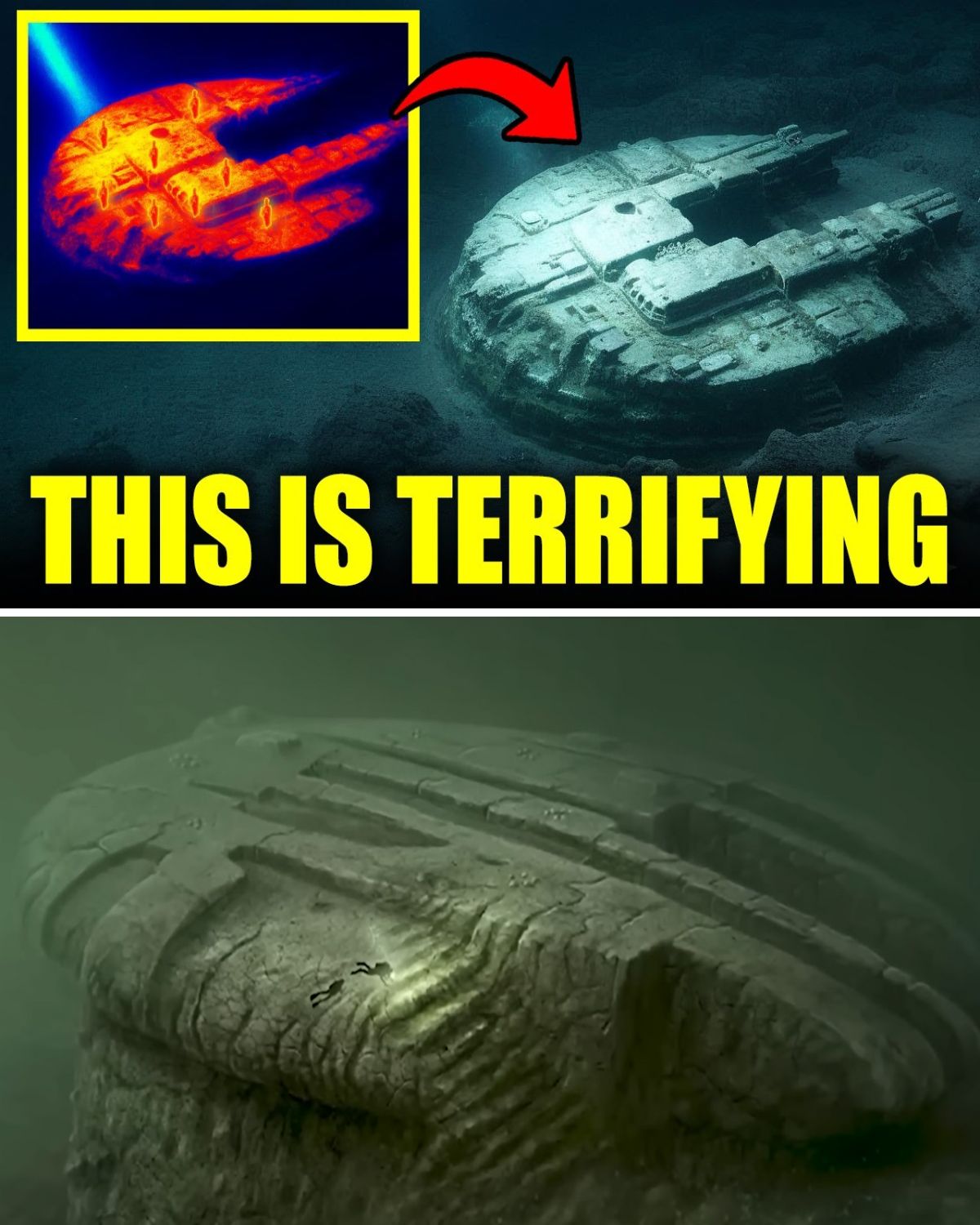
The Baltic Sea anomaly, a mysterious underwater structure that has puzzled scientists for over a decade, has recently been subjected to groundbreaking AI scans that suggest it may not be of human origin. The discovery has reignited interest in this enigmatic formation, previously thought to be a mere geological curiosity.
 Located approximately 300 feet below the surface, the anomaly is a massive disc-shaped object measuring around 60 meters wide. Its symmetry and distinct features have led to comparisons with spacecraft and ancient architecture. The initial discovery in 2011 by Swedish explorers Peter Lindberg and Dennis Asberg revealed a near-perfect circular shape, raising questions about its origins.
Located approximately 300 feet below the surface, the anomaly is a massive disc-shaped object measuring around 60 meters wide. Its symmetry and distinct features have led to comparisons with spacecraft and ancient architecture. The initial discovery in 2011 by Swedish explorers Peter Lindberg and Dennis Asberg revealed a near-perfect circular shape, raising questions about its origins.
The recent AI analysis, conducted in collaboration with astronomer Dr. Beatatric Villa Royel, has added a new dimension to the investigation. The AI tools have uncovered intricate patterns and geometric alignments previously missed, suggesting a level of design that challenges conventional explanations. Asberg’s reaction to the findings indicates that something significant has been revealed, heightening anticipation among researchers and enthusiasts alike.
Despite prior theories labeling the anomaly as a natural formation shaped by glacial activity, the AI data presents compelling evidence to the contrary. The presence of metallic compounds in sediment samples further complicates the narrative, hinting at a potential artificial origin. This has led to renewed speculation about ancient civilizations or even extraterrestrial involvement.
The anomaly’s effect on electronic devices has also intrigued researchers. Reports of erratic compass behavior and malfunctioning equipment near the site suggest an unexplained energy field. Such phenomena have been documented at other mysterious underwater locations, prompting questions about a possible network of similar structures.
The renewed interest in the Baltic Sea anomaly underscores a critical truth: the oceans remain largely unexplored. With nearly 70% of the Earth’s surface underwater, the potential for discovering more anomalies is vast. As AI technology advances, researchers are optimistic about uncovering the secrets of the deep sea.
The next steps involve rigorous scientific analysis and transparency in sharing results with the public. As teams continue to explore the anomaly, the hope is that definitive answers will emerge, shedding light on the object’s origin and its implications for our understanding of human history and the natural world.
In a world where the truth often lies beneath the surface, the Baltic Sea anomaly stands as a testament to the mysteries that await discovery. As researchers delve deeper, the question remains: what else lies hidden in the depths of our oceans?